On-premises DNS Simulation
AWS PrivateLink endpoints have a fixed IP address in each Availability Zone where they are deployed, for the life of the endpoint (until it is deleted). These IP addresses are attached to Elastic Network Interfaces (ENIs). AWS recommends using DNS to resolve the IP addresses for endpoints so that downstream applications use the latest IP addresses when ENIs are added to new AZs, or deleted over time.
In this section, you will create a forwarding rule to send DNS resolution requests from a simulated on-premises environment to a Route 53 Private Hosted Zone. This section leverages the infrastructure deployed by CloudFormation in the Prepare the environment section.
Create DNS Alias Records for the Interface endpoint
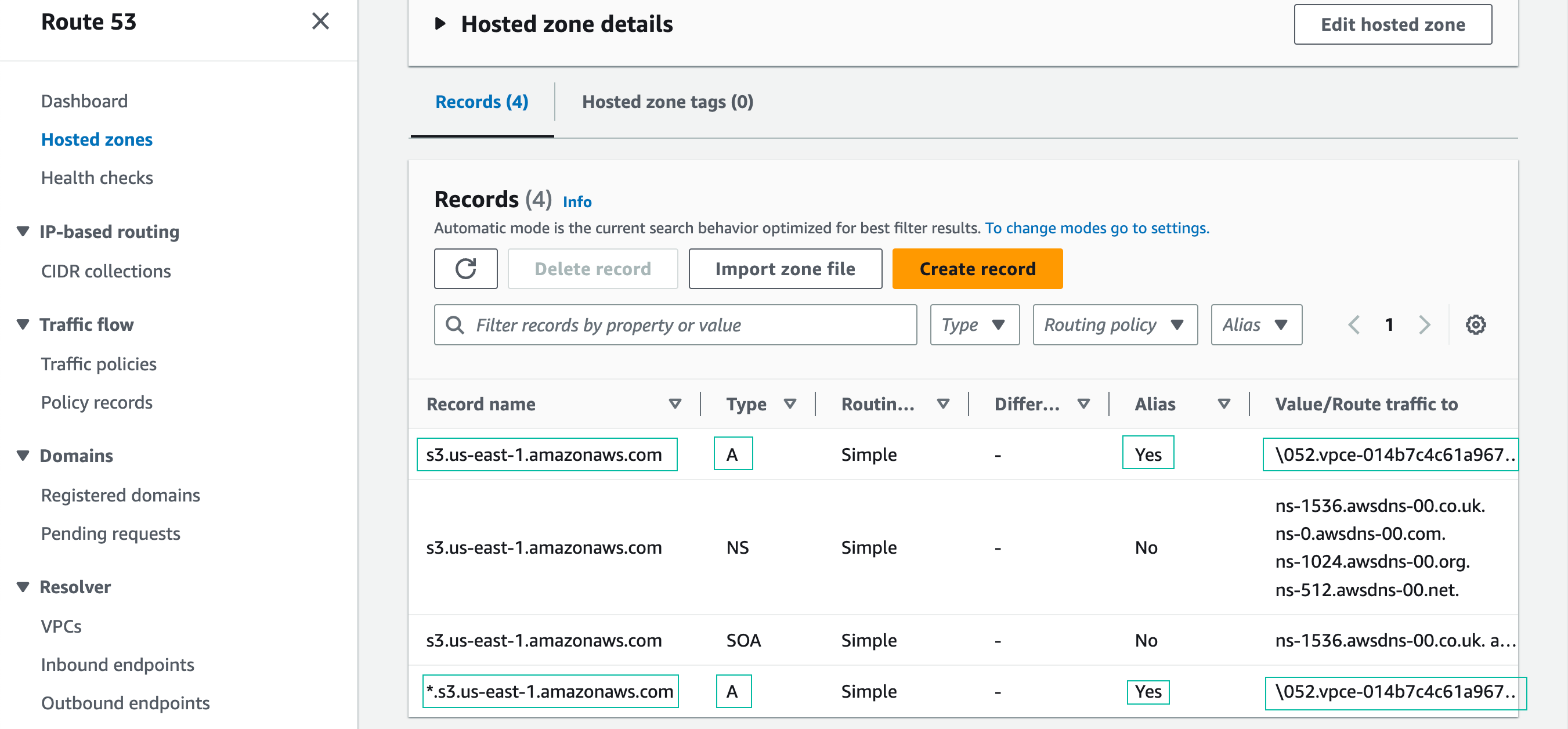
- Navigate to the Route 53 management console (Hosted Zones section). The CloudFormation template you deployed in the Prepare the environment section created this Private Hosted Zone. Click on the name of the Private Hosted Zone, s3.us-east-1.amazonaws.com:
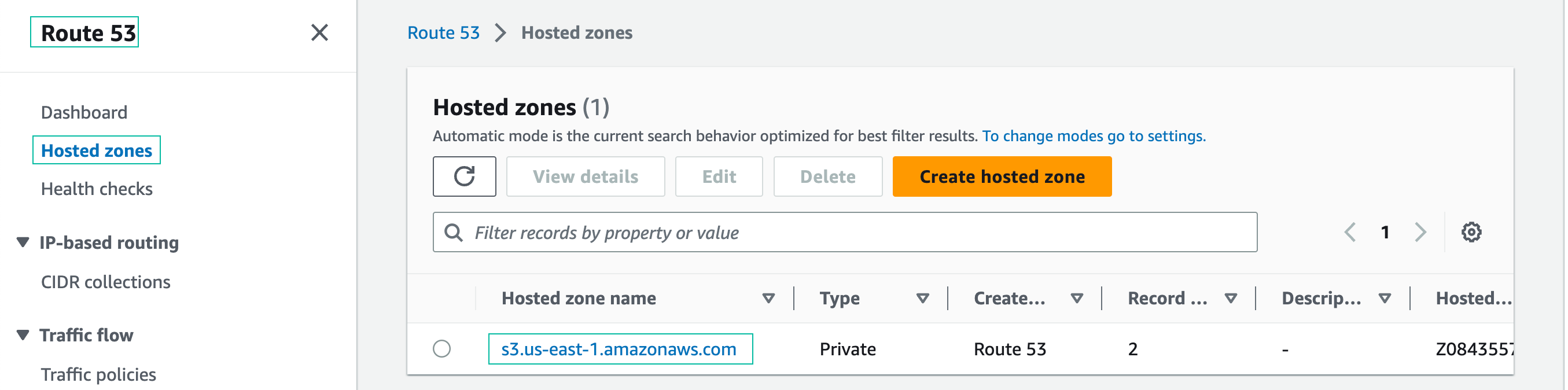
- Create a new record in the Private Hosted Zone:
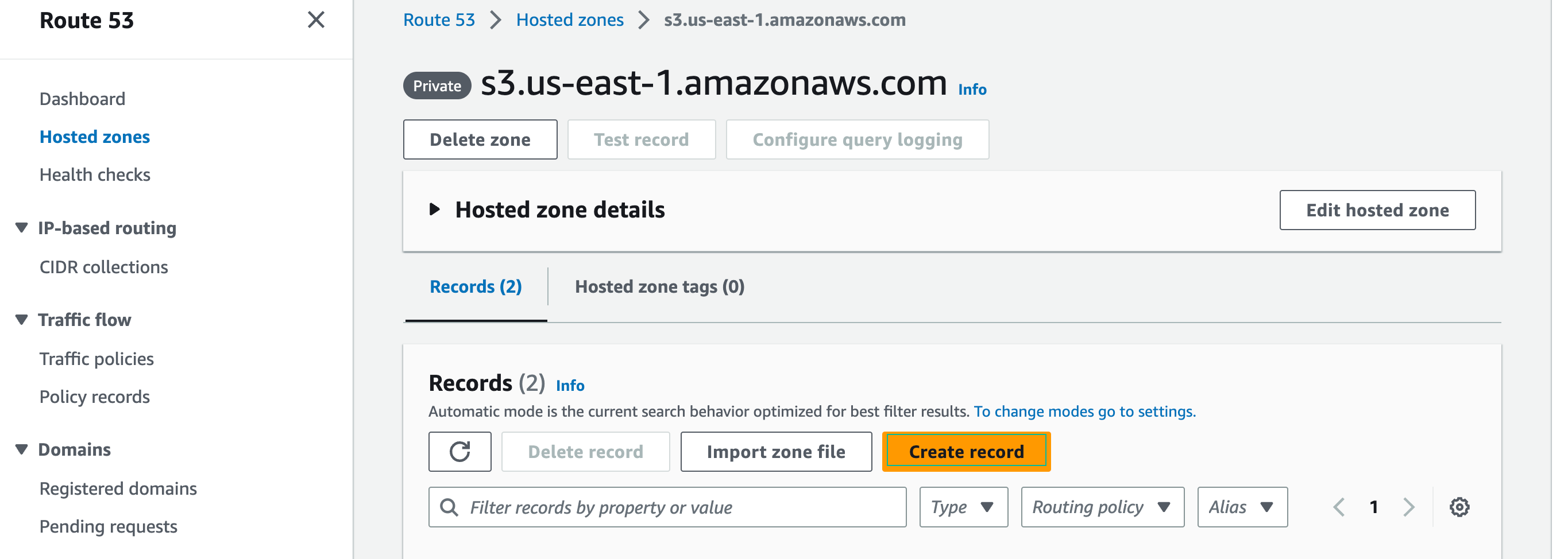
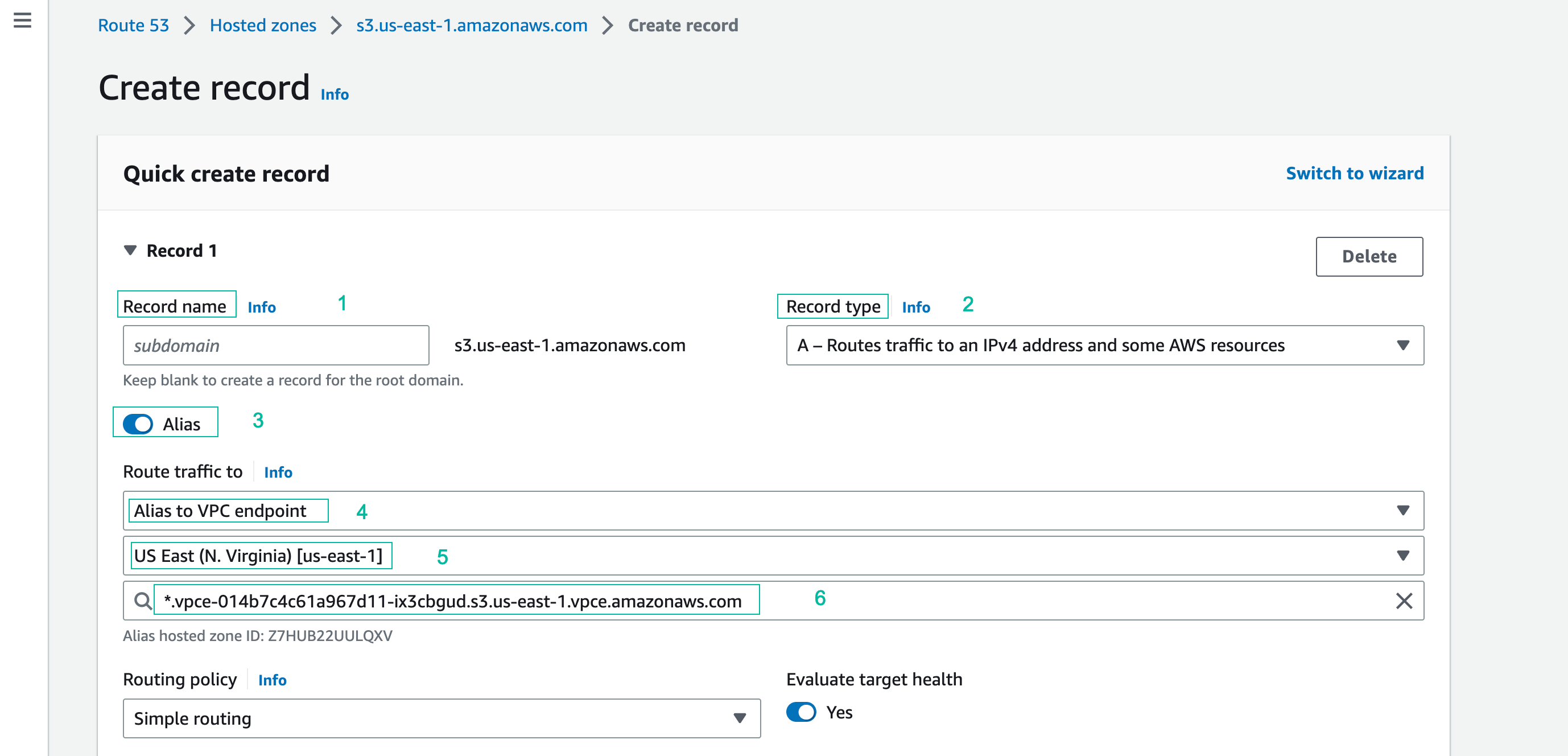
- Record name and record type keep default options
- Alias Button: Click to enable
- Route traffic to: Alias to VPC Endpoint
- Region: US East (N. Virginia) [us-east-1]
- Choose endpoint: Paste the Regional VPC Endpoint DNS name from your text editor (you saved when doing section 4.3)
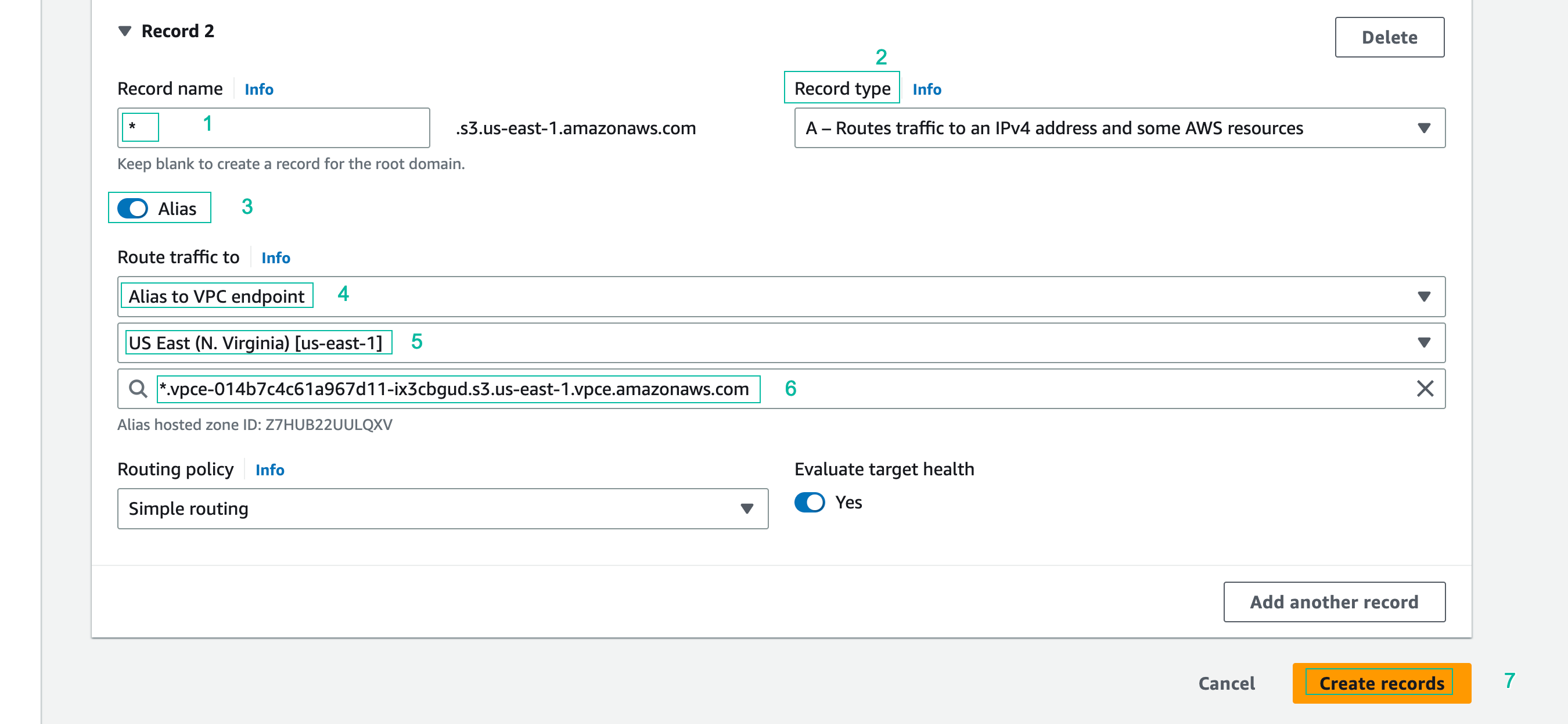
- Click Add another record, and add a second record using the following values. Click Create records when finished to create both records.
- Record name: *.
- Record type: keep default value (type A)
- Alias Button: Click to enable
- Route traffic to: Alias to VPC Endpoint
- Region: US East (N. Virginia) [us-east-1]
- Choose endpoint: Paste the Regional VPC Endpoint DNS name from your text editor
The new records appear in the Route 53 console:
Create a Resolver Forwarding Rule
Route 53 Resolver Forwarding Rules allow you to forward DNS queries from your VPC to other sources for name resolution. Outside of a workshop environment, you might use this feature to forward DNS queries from your VPC to DNS servers running on-premises. In this section, you will simulate an on-premises conditional forwarder by creating a forwarding rule that forwards DNS queries for Amazon S3 to a Private Hosted Zone running in “VPC Cloud” in-order to resolve the PrivateLink interface endpoint regional DNS name.
- From the Route 53 management console, click Inbound endpoints on the left side bar
- In the Inbound endpoints console, click the ID of the inbound endpoint
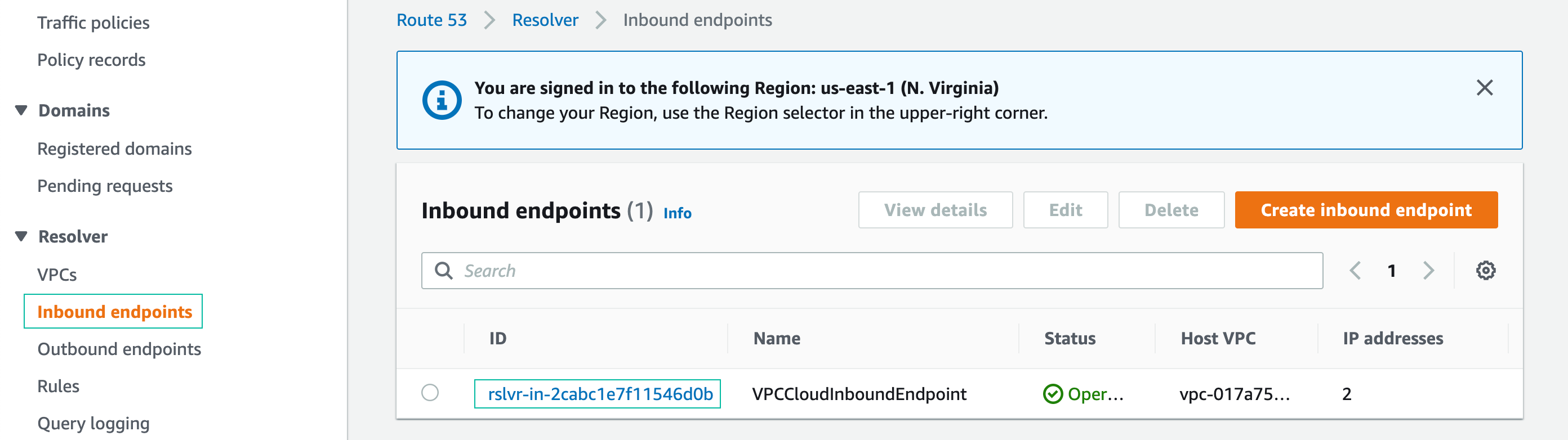
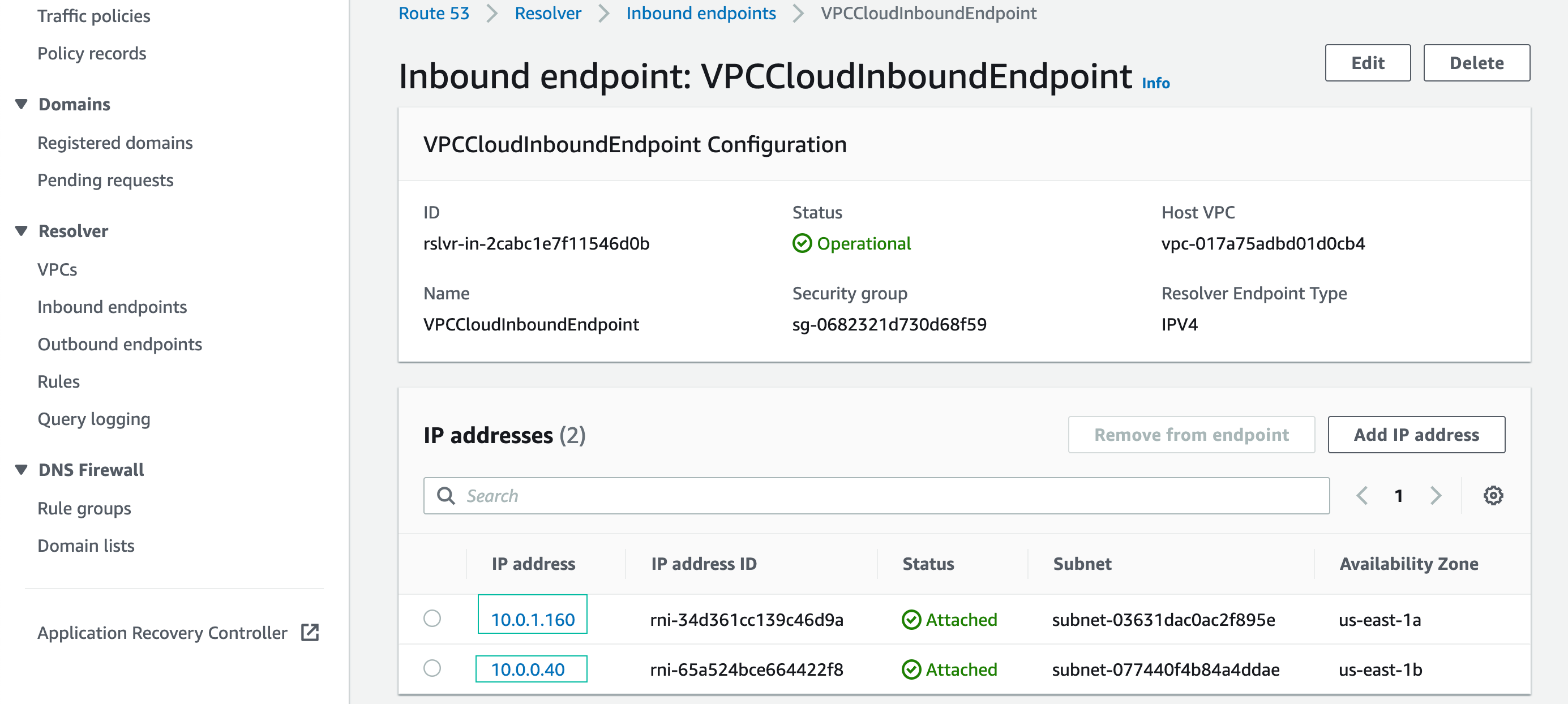
- Copy the two IP addresses listed to your text editor
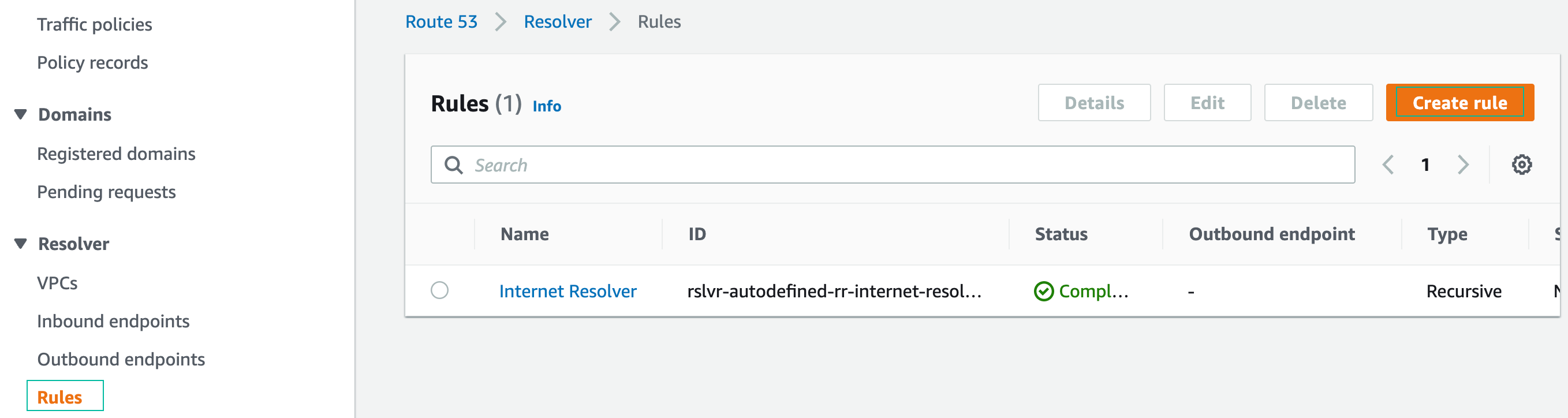
- From the Route 53 menu, choose Resolver > Rules, and click Create rule:
- In the Create rule console:
- Name: myS3Rule
- Rule type: Forward
- Domain name: s3.us-east-1.amazonaws.com
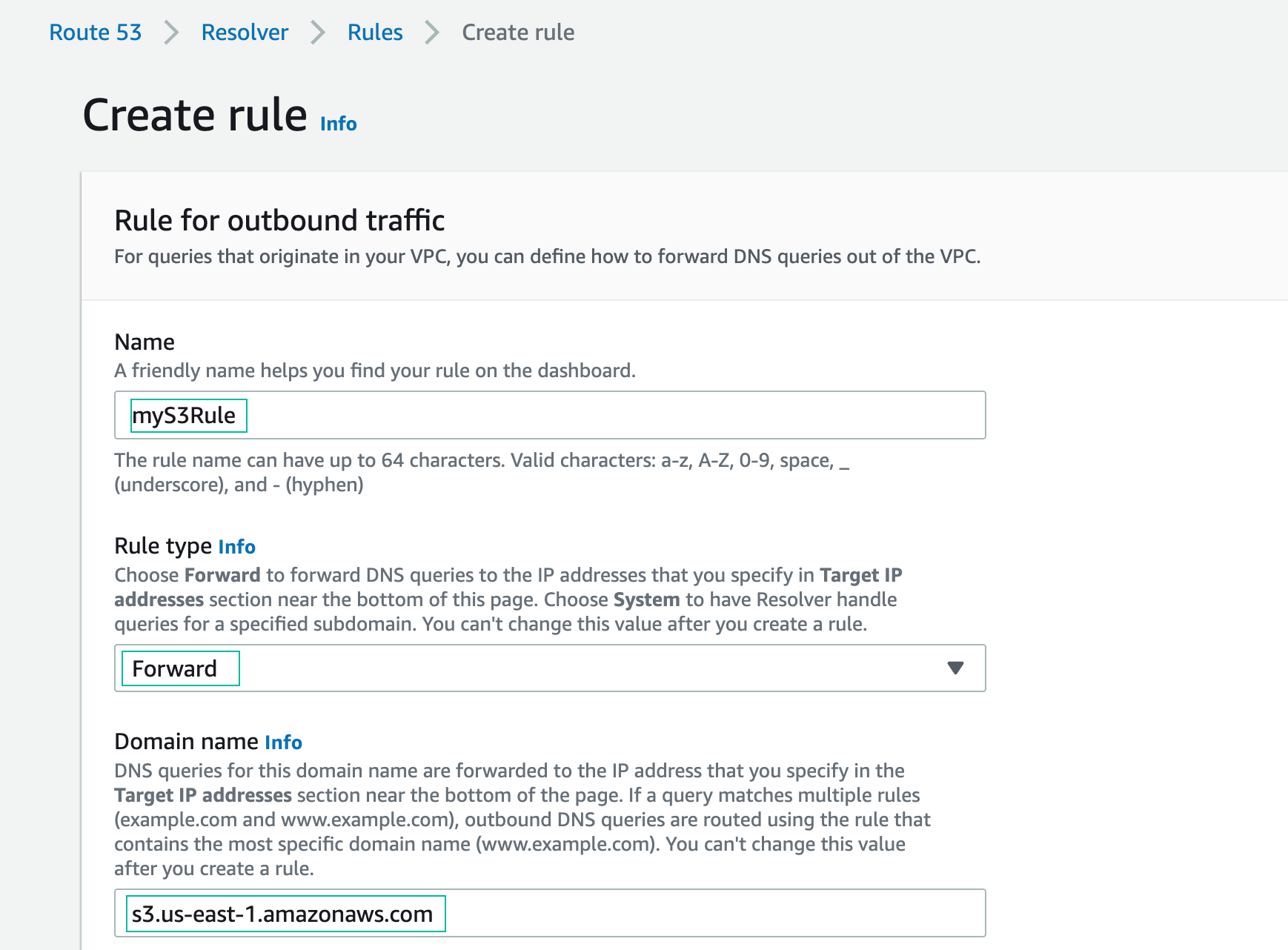
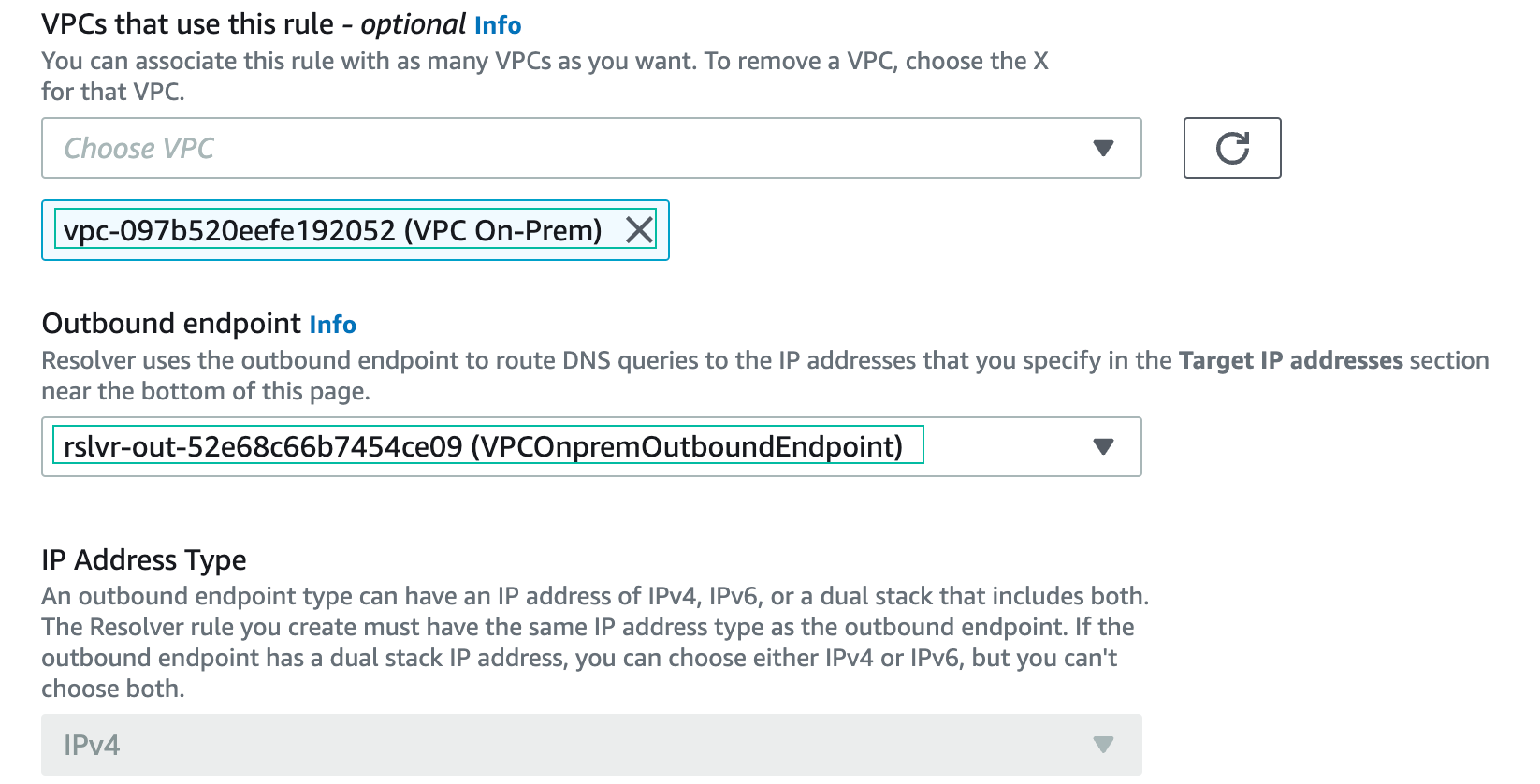
- VPC: VPC On-prem
- Outbound endpoint: VPCOnpremOutboundEndpoint
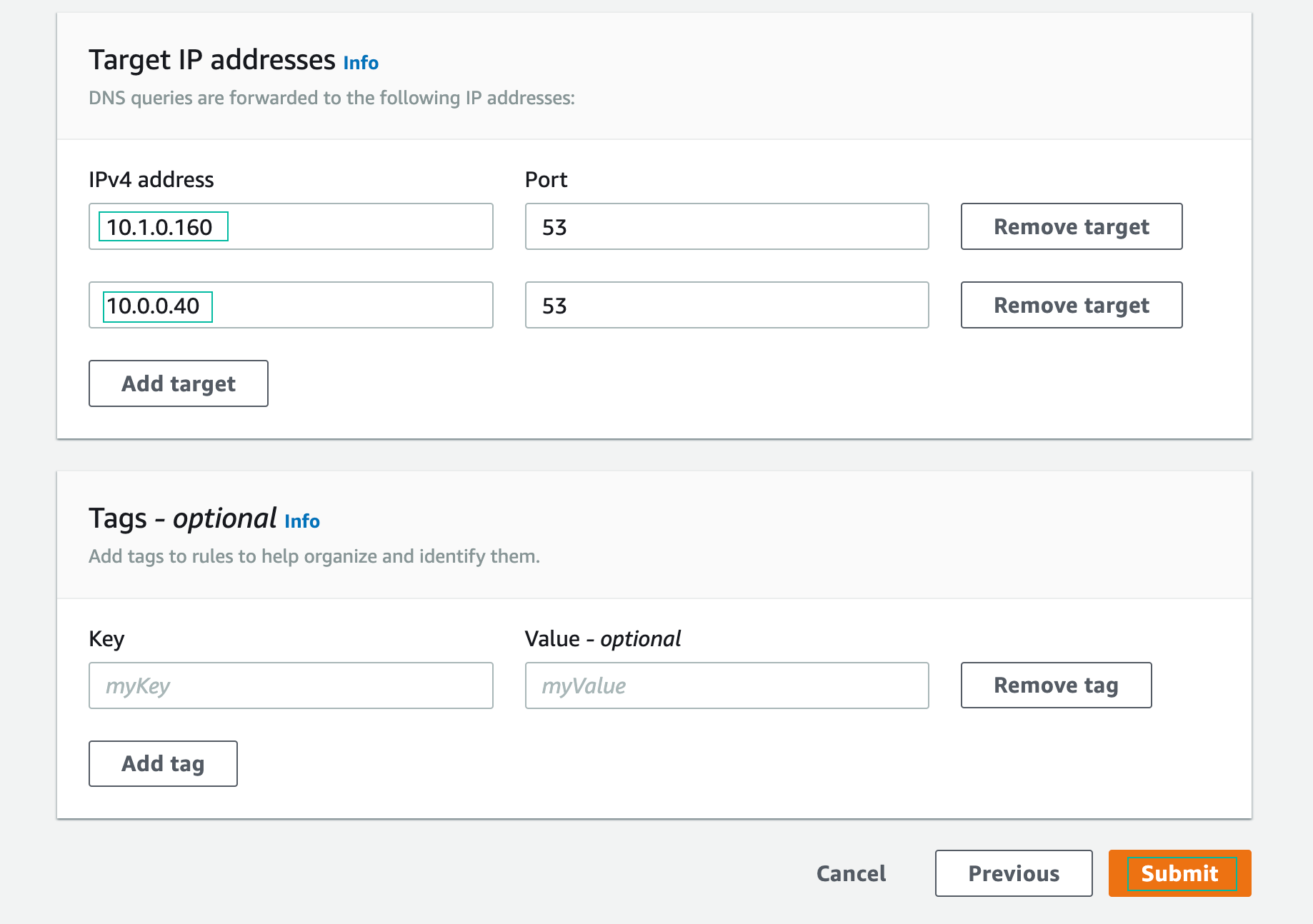
- Target IP Addresses: Enter both IP addresses from your text editor (inbound endpoint addresses) and then click Submit
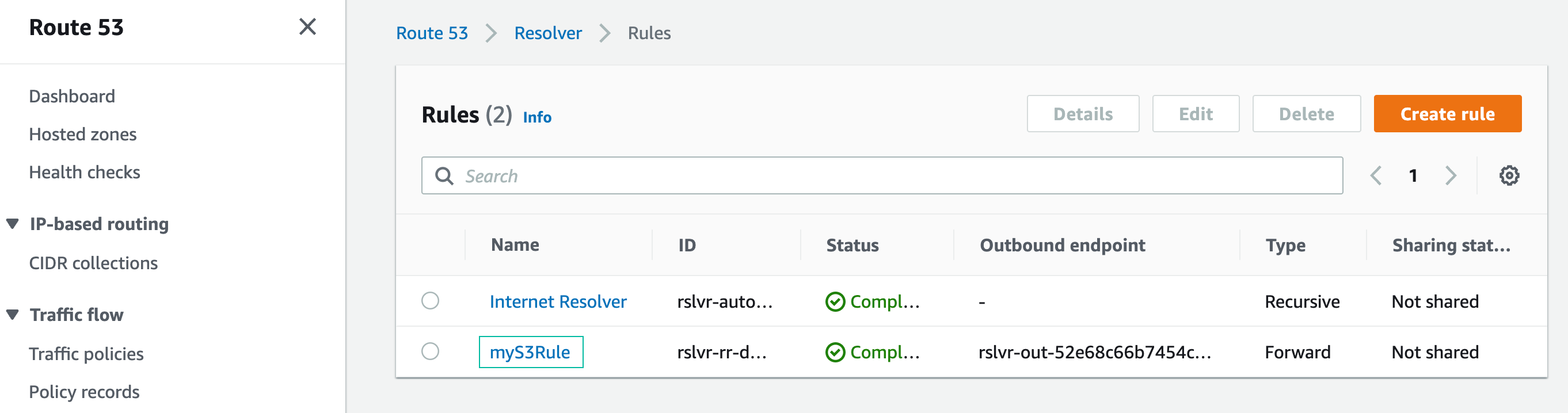
 You have successfully created resolver forwarding rule.
You have successfully created resolver forwarding rule.
Test the on-premises DNS Simulation
- Connect to Test-Interface-Endpoint EC2 instance with Session manager
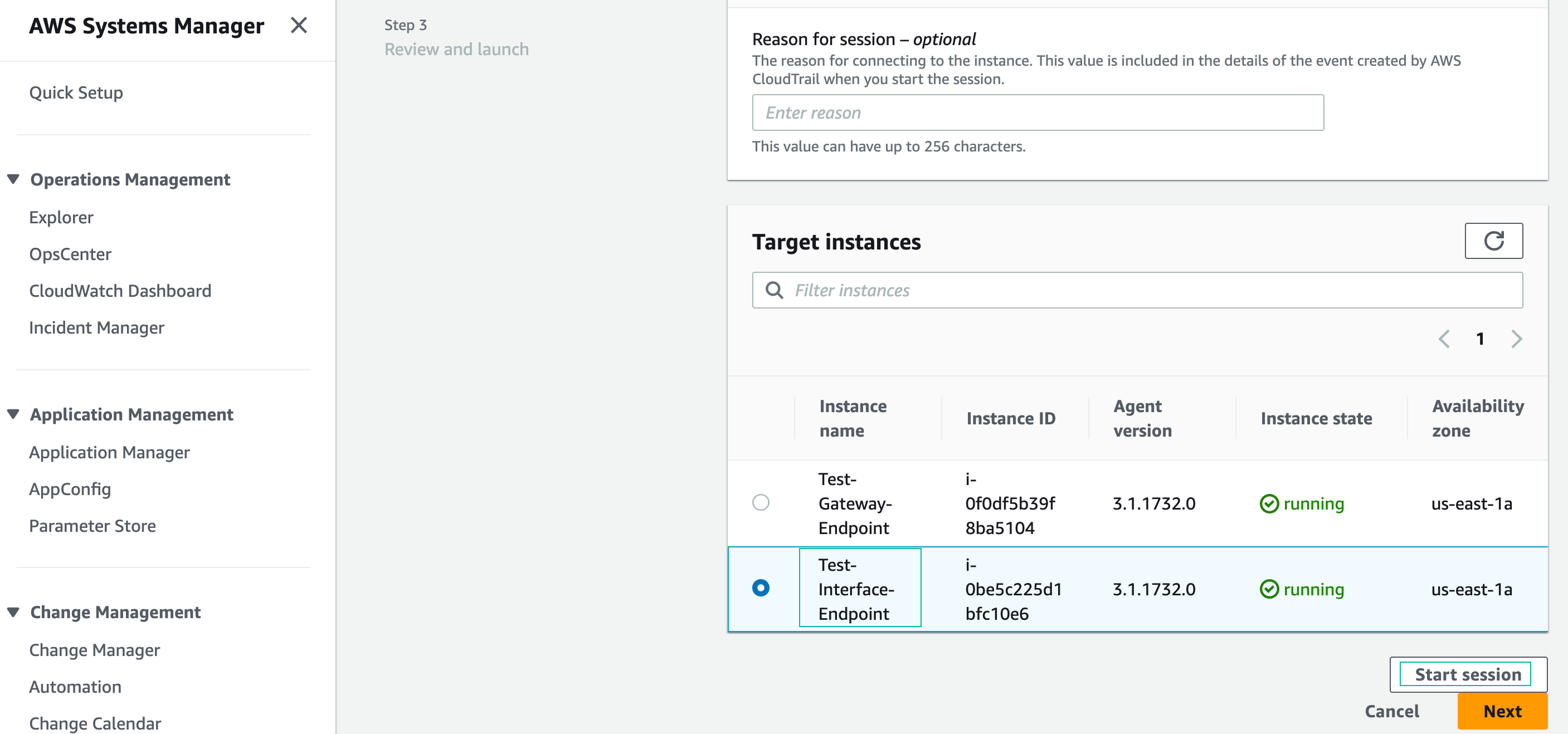
- Test DNS resolution. The dig command will return the IP addresses assigned to the VPC Interface endpoint running in VPC Cloud (your IP’s will be different): dig +short s3.us-east-1.amazonaws.com
The IP addresses returned are the VPC endpoint IP addresses, NOT the Resolver IP addresses you pasted from your text editor. The IP addresses of the Resolver endpoint and the VPC endpoint look similar because they are all from the VPC Cloud CIDR block.

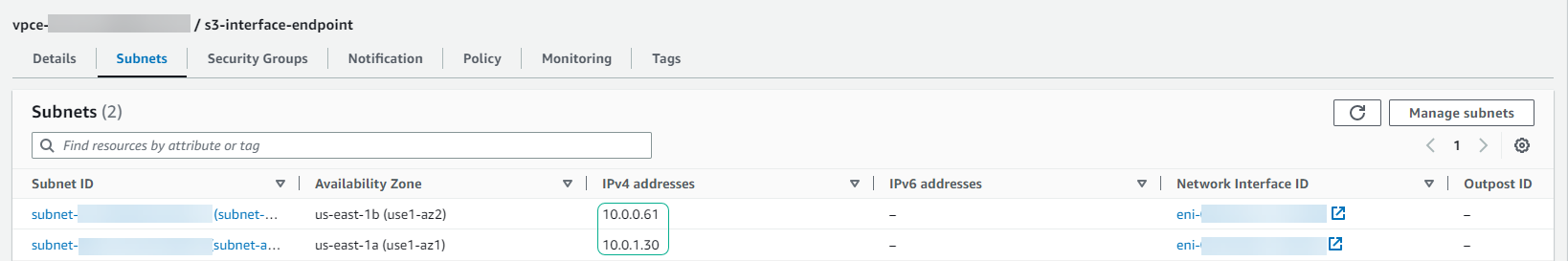
- Navigate to the VPC menu (Endpoints section), select the S3 Interface endpoint. Click the Subnets tab and verify that the IP addresses returned by Dig match the VPC endpoint:
- Return to your shell and use the AWS CLI to test listing your S3 buckets:
aws s3 ls --endpoint-url https://s3.us-east-1.amazonaws.com

- Terminate your Session Manager session:

In this section you created an Interface endpoint for Amazon S3. This endpoint can be reached from on-premises through Site-to-Site VPN or AWS Direct Connect. Route 53 Resolver outbound endpoints simulated forwarding DNS requests from on-premises to a Private Hosted Zone running the cloud. Route 53 inbound Endpoints recieved the resolution request and returned a response containing the IP addresses of the VPC interface endpoint. Using DNS to resolve the endpoint IP addresses provides high availability in-case of an Availability Zone outage.